Preterm birth can cause health problems later in life, should be considered in adult health records, URI study shows
KINGSTON, R.I. — August 4, 2025 — The stress preterm infants experience at birth can carry on throughout a lifetime and cause negative health impacts later in life, necessitating the routine inclusion of birth history in medical records and the development of clinical guidelines for adults born preterm, the longest continuously running study of individuals born preterm in the United States has shown.
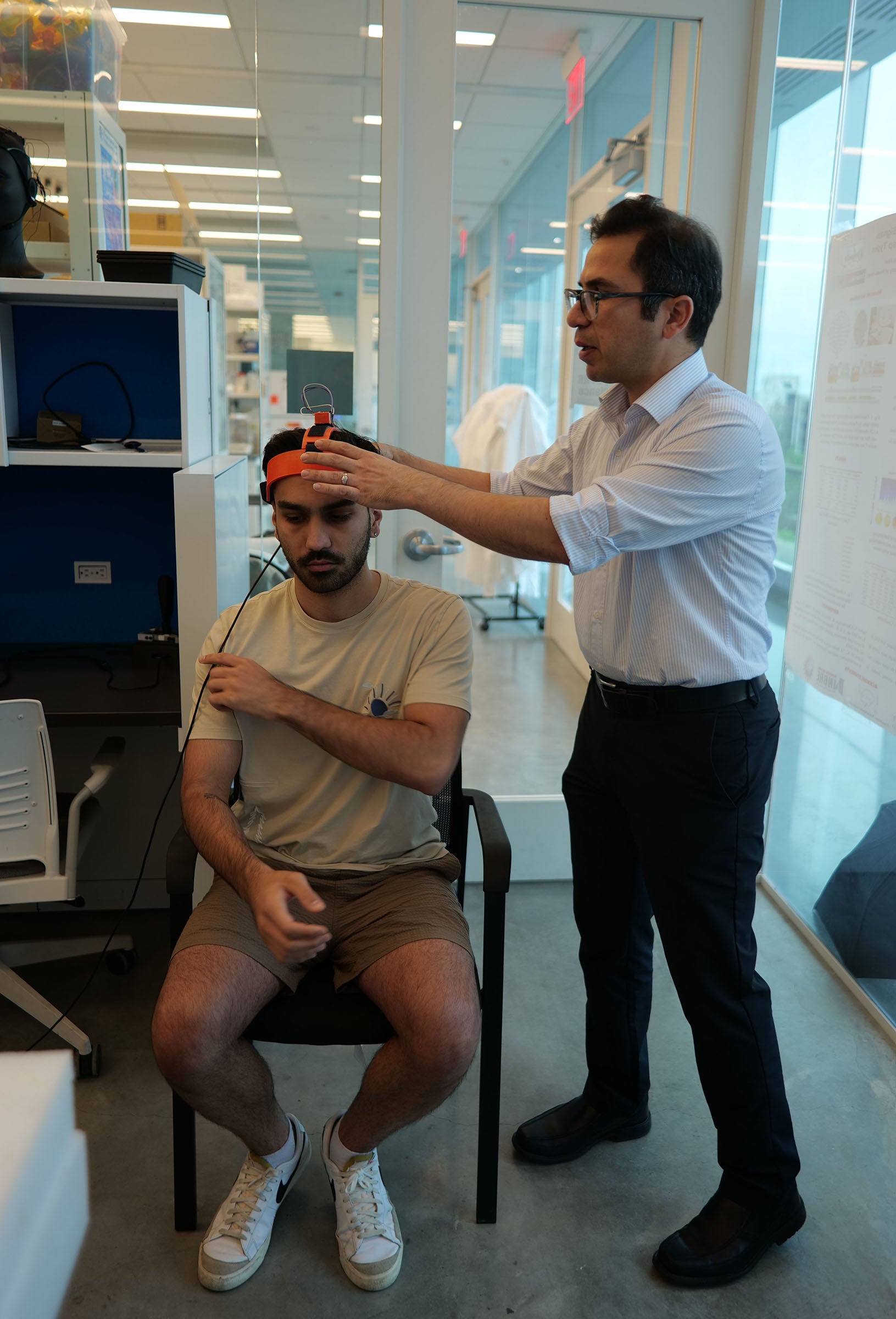
University of Rhode Island College of Nursing Professor Amy D’Agata is continuing the work that began in the 1980s with a group of babies born preterm at Women & Infants Hospital. Involving 215 people born 35 years ago—including a control group of full-term babies, and preterm babies born at 22 to 36 weeks—the study tracks the successes and difficulties preterm babies continue to face into adulthood, and compares them to the group of participants born full term. The project has so far garnered more than $10 million in research grant funding.
D’Agata, who took over as principal researcher after the retirement of Professor Emeritus Mary Sullivan, has published the most recent results in the Journal of the American Medical Association. The published paper focuses physiological and psychological health outcomes that D’Agata and her team of researchers have identified as the study participants approach 40 years old. Those born preterm have shown a higher risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, increased abdominal fat, and low bone density. Psychologically, the group tends to internalize problems, often resulting in increased levels of depression and anxiety.
“Preterm birth is not just a neonatal issue. It, in fact, is a lifelong condition,” D’Agata said the study shows. “For individuals who have medical complications early in life, we are now seeing an increased risk of different chronic health issues later in life. We are now realizing that there is a very strong link between what happens to you early in life and later health outcomes.”
The study offers important takeaways for health-care clinicians, who are not always aware a patient was born preterm because birth history is not commonly included in adult medical records. D’Agata’s study is showing the need to include the information, and to develop adult screening guidelines for individuals who have a history of preterm birth. The work is also helping people who have been impacted by preterm birth understand that their birth history should be included in their medical records and should be considered in the context of their overall health.
“In this country, millions of people born preterm have grown into adulthood and are now seeing clinicians across primary care and various specialties, yet providers rarely ask about birth history,” D’Agata said. “We are urging that birth history be included as a standard question on every adult intake form. Health cannot be fully optimized if we overlook such a critical assessment piece. Understanding an individual’s birth history, alongside growing research identifying increased health risks for those born preterm and the development of targeted clinical guidelines, will advance health equity for survivors of early birth. We believe a paradigm shift is needed in health care that recognizes preterm birth as a chronic condition requiring lifelong monitoring and support.”
While the study’s most recent results were just published in JAMA Network Open in July, D’Agata is already looking toward the next set of findings. Continuing to work with fellow URI professor Justin Parent, D’Agata is examining epigenetic age acceleration among individuals born preterm. Understanding any differences in epigenetic aging that may exist between preterm and full-term born adults may be another approach to understanding long-term health.
Latest All News
- URI engineering professor recipient of NSF CAREER Award for assistive and rehabilitative robotics researchKINGSTON, R.I. – August 6, 2025 – Severe motor impairment such as paralysis and degenerative conditions can limit a person’s ability to perform certain dexterous tasks. Currently, there are technological advancements that can aid in restoring some of this ability, but they can be invasive, requiring surgical implants that create drawbacks. University of Rhode Island […]
- Engineering professor Weiwei Jia receives NSF CAREER Award to advance cloud computing applications, systemsKINGSTON, R.I. – Aug. 6, 2025 – With the rapid advancement and widespread integration of artificial intelligence and cloud technologies, new challenges and performance demands are emerging that cannot be effectively addressed by traditional solutions. Systems used in the cloud are designed for legacy applications and traditional hardware. Cloud providers consistently struggle to meet the […]
- John Olerio named to Providence Business News 40 Under Forty listKINGSTON, R.I. – July 31, 2025 – University of Rhode Island Executive Director of Strategic Initiatives John Olerio M.B.A. ’11, Ph.D. ’20 has been recognized with a PBN 40 Under Forty Award by Providence Business News. The annual award recognizes individuals under the age of 40 who have excelled in their profession and are involved […]
- Core matters: URI geoscientist weighs in on critical mineralsKINGSTON, R.I. – July 31, 2025 – Critical minerals are a hot topic in the news these days, whether as a point of contention between countries or in discussions of supply and demand. Critical minerals are nonfuel minerals/metals necessary to industry and are essential in a wide range of technologies. Their availability is sensitive to […]
- URI jazz students to return to Newport Jazz Festival for third yearKINGSTON, R.I. – July 31, 2025 – University of Rhode Island music students will again take the stage at the legendary Newport Jazz Festival. Playing a half-hour set that tips the hat to the festival’s vast history, the seven URI students will perform Sunday, Aug. 3, at about 2:45 p.m. on the Foundation Stage at […]
- Caribbean coral reefs’ chronic decline could get a boost from proactive assisted gene flow — if allowedKINGSTON, R.I. – July 30, 2025 – Coral reefs are under threat from warming oceans and prolonged heat — but regulatory inaction also poses a risk. However, marine biologists say that new approaches in the region could help prevent species loss and retain ecosystem function, if they get the permission to proceed. One approach that […]